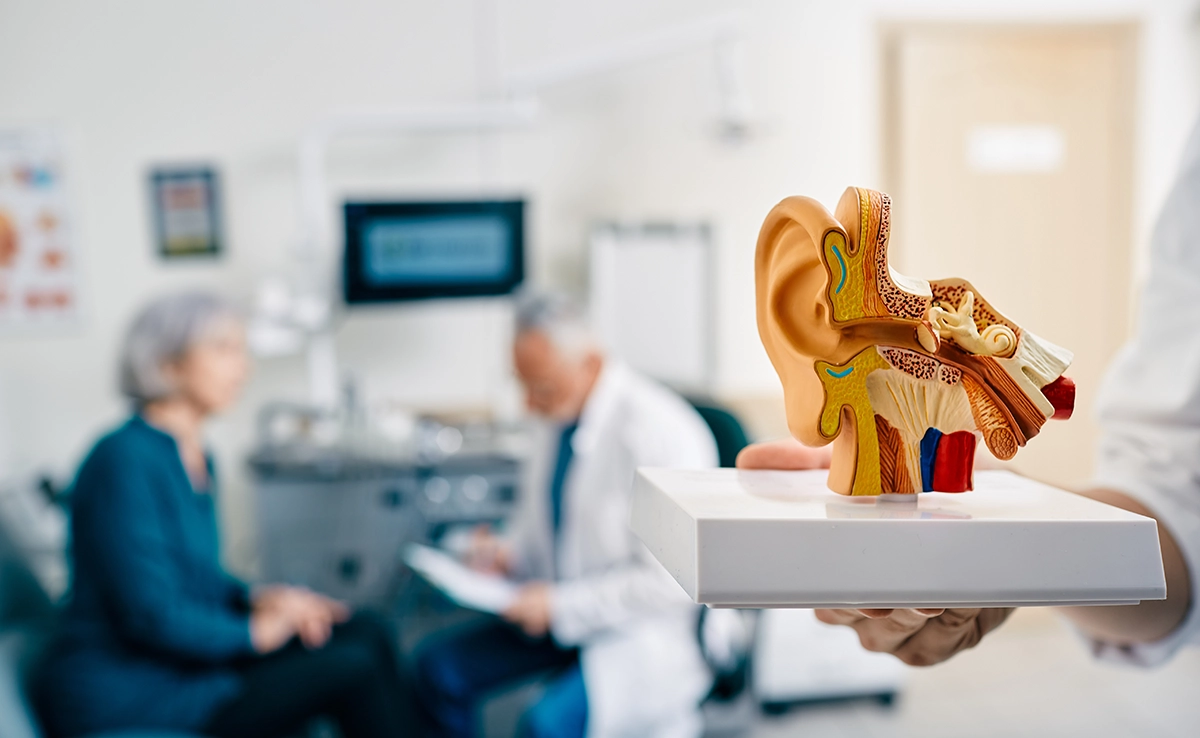
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is the most common type of hearing loss. In fact, over 66,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with sensorineural hearing loss every year. In this article, we will provide a detailed overview of what sensorineural hearing loss is, common symptoms to look out for, and how it can be treated.
Understanding Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The two most common types of hearing loss are sensorineural and conductive. While conductive hearing loss is not always permanent, SNHL is typically irreversible and will become progressively more severe over time. This can significantly impact not only your hearing but your overall quality of life as well. While SNHL is progressive, proper intervention can minimize its impact on communication and long-term effects.
Symptoms of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss symptoms can be difficult to notice at first, but they will gradually intensify as hearing loss develops. Routine hearing exams and knowing how to spot the signs and symptoms of SNHL are crucial to ensuring the longevity of your hearing health.
Some of the most common symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss include:
- Muffled hearing
- Difficulty comprehending speech
- Congested or blocked sensation in the ear
- Abrupt or gradual hearing loss
- Ringing in the ear
- Dizziness
- Difficulty hearing certain consonants like S, H, or F
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, schedule an appointment for a hearing test as soon as possible to get a head start on treatment.
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
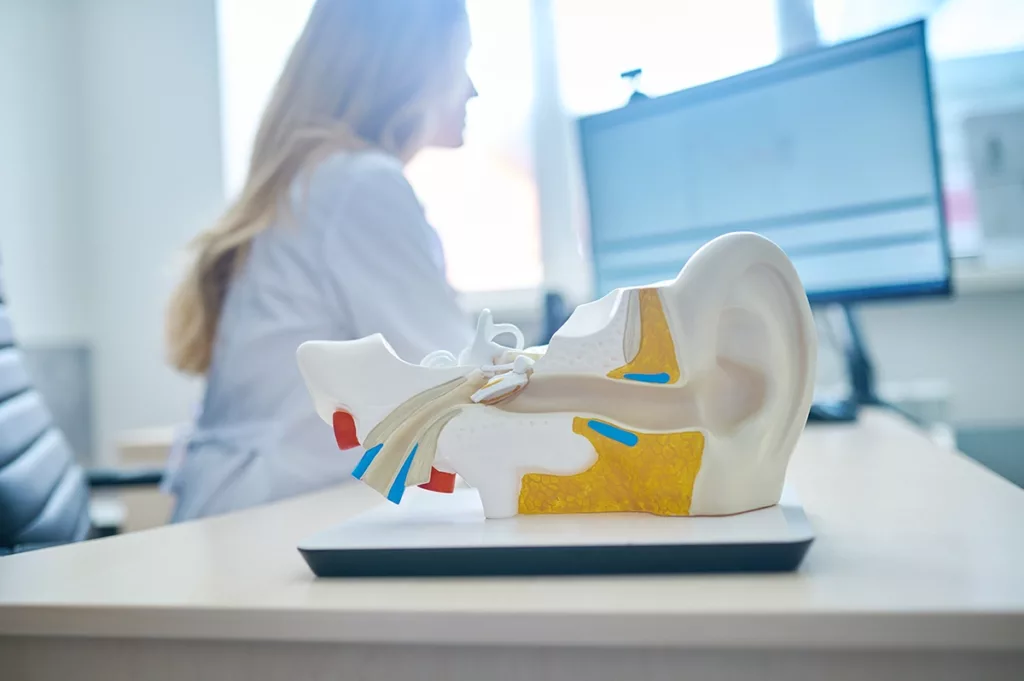

Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the auditory nerve, and/or the microscopic hair cells located in the inner ear (cochlea). The inner ear is responsible for converting sound waves into signals that are then sent to the brain for processing. When our inner ear is compromised, it can have severe consequences on hearing, balance, and our well-being overall.
Damage to the inner ear resulting in SNHL can be caused by a variety of factors. Below, we list the most common causes of sensorineural hearing loss:
Aging (Presbycusis)
The most common cause of hearing loss worldwide is age-related hearing loss, also known as presbycusis. This condition affects an estimated two-thirds of adults in the United States who are 70 or older. It’s important to note however that some patients report noticing symptoms as early as age 60.
As we age, our inner hair cells will naturally degrade. This typically manifests as a gradual decline in hearing quality, especially in loud environments with a lot of background noise, as well as with high-frequency sounds. Most patients describe this as a loss of clarity as opposed to volume. Many individuals with presbycusis also report experiencing ringing in one or both ears (tinnitus).
Routine hearing tests are crucial for catching signs of age-related sensorineural hearing loss early on. The general recommendation is that adults under the age of 50 should undergo a hearing test every three to five years. After age 60 is reached, annual hearing exams are recommended, whether or not noticeable symptoms are present.
The table below shows how often you should get your hearing tested based on your age if you don’t have any symptoms and are at a low risk of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL):
Recommended Hearing Test Frequency for Adults
| Age | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 18-25 | 1 baseline hearing test to serve as a reference for future tests |
| 26-50 | Every 3-5 years with no symptoms of hearing loss |
| 51-60 | Every year, with or without symptoms of hearing loss |
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
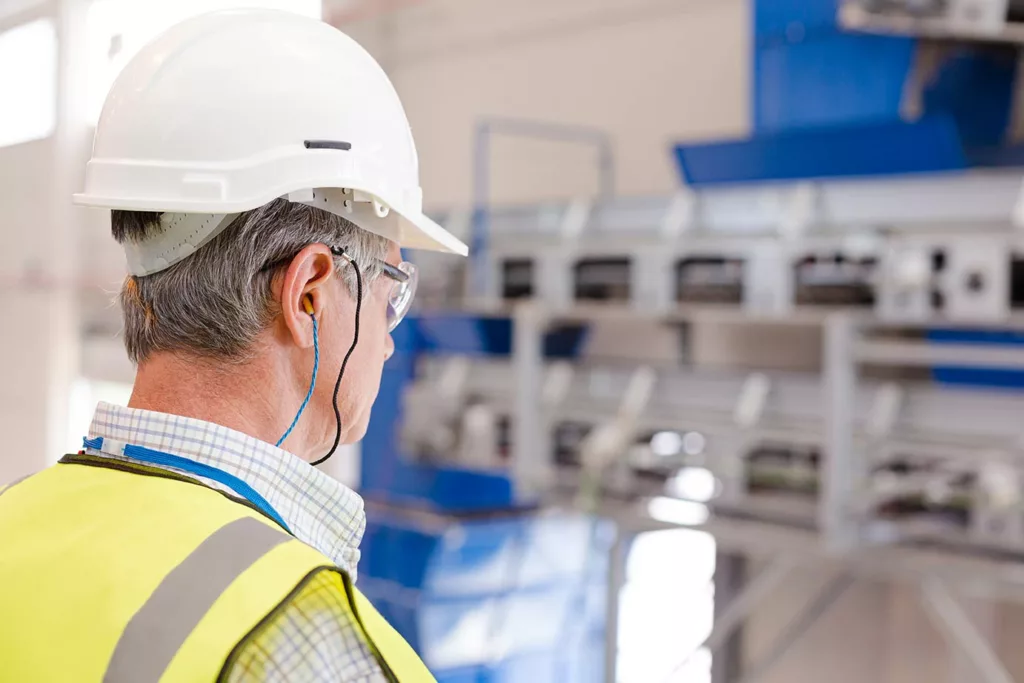

Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is another form of SNHL that occurs when the inner ear is damaged by excessive exposure to loud noise. This damage can result in a range of symptoms like difficulty hearing certain frequencies, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and even complete hearing loss.
According to the CDC, it’s estimated that 12.5% (5.2 million) of children and adolescents aged 6–19 years and 17% of adults aged 20–69 years (26 million) experience permanent hearing loss due to noise-induced harm. Worldwide, 16% of adults with hearing loss are exposed to occupational noise damage.
To prevent these harmful effects, it’s important to schedule routine hearing exams to monitor your hearing quality and take proactive measures to protect your hearing around loud noises. Experts suggest limiting your exposure to sounds above 85 dBA, and wearing proper hearing protection whenever in noisy environments or while participating in loud activities.
The following table shows the average decibel ratings of common sounds for reference:
Average Decibel Ratings of Common Sounds
| dBA | Sound |
|---|---|
| 60-70 dBA | Normal conversation |
| 71-80 dBA | Dishwasher |
| 81-90 dBA | Kitchen blender |
| 91-110 dBA | Hairdryers, power tools |
| 111-120 dBA | Motorcycles 121-130 |
| 121-130 dBA | Concerts, thunder |
Medical Conditions
Certain illnesses, infections, and medical conditions can cause inner ear damage that leads to sensorineural hearing loss. Here are just a few of some common medical conditions that can cause SNHL:
- Viral infections (such as measles or mumps)
- Shingles
- Meningitis
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- High fever or elevated body temperature
- Ménière’s disease
- Obesity
- Hypertension
- And more
If you’ve had any of these conditions, make sure to report them to your hearing specialist. It’s also vital that you keep an eye out for symptoms of possible hearing loss and attend routine hearing exams to catch any signs of SNHL.
Ototoxic Medications
Certain medications have side effects that can cause damage to the inner ear resulting in sensorineural hearing loss. Drugs with this effect are referred to as ototoxic medications and can lead to symptoms like ringing in the ear, poor balance, and irreversible hearing loss. It’s crucial to be aware of the medications you are taking and keep an eye out for symptoms of hearing loss. Immediately report any changes in your hearing to your primary care provider or seek emergency care.
Injury or Trauma
Often, injury or head trauma can cause structural damage to the inner ear. Ruptured eardrums, hair cell damage, or restricted blood flow can all damage our auditory nerve, resulting in sensorineural hearing loss. It’s important to lower your risk of injury and inner ear trauma by avoiding unsafe situations and always wearing properly fitting head protection like helmets and ear guards when required.
Diagnosing Sensorineural Hearing Loss
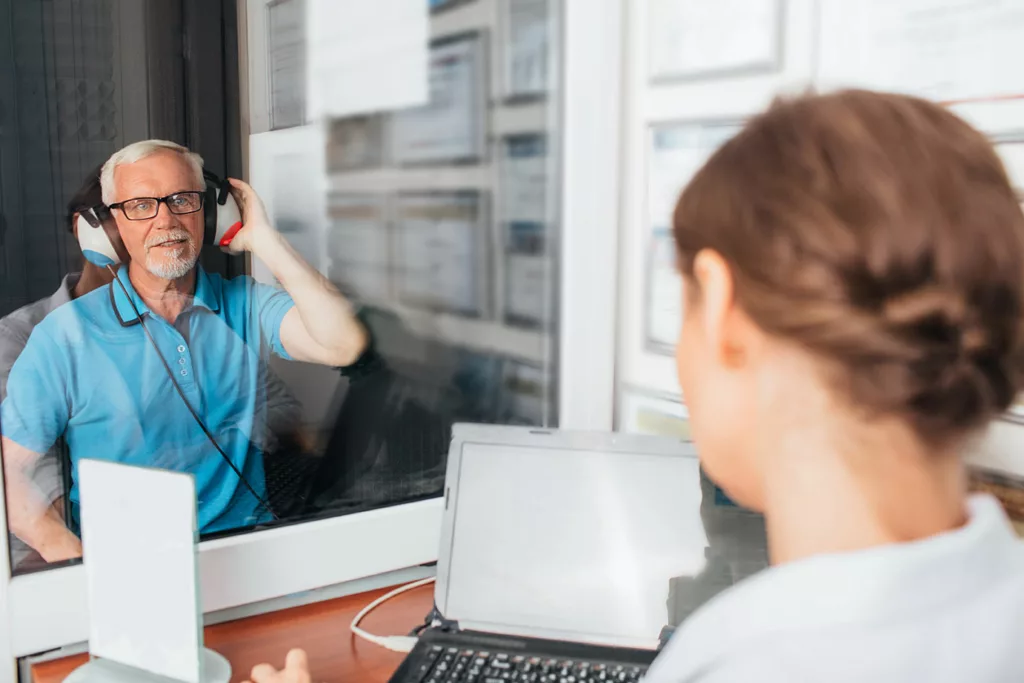

Sensorineural hearing loss can only be diagnosed during a comprehensive hearing test conducted by a professional, such as a hearing healthcare specialist. Early detection is crucial because it allows for appropriate treatment to be implemented in a timely manner. Interventions like hearing aids can also significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with SNHL.
A comprehensive hearing exam is designed to evaluate your hearing abilities and overall auditory health. After reviewing your medical history, your hearing health specialist will ask you questions about your hearing concerns before performing a series of assessments. The goal is to identify any presence of hearing loss, its degree of development, and the underlying cause to create an appropriate treatment plan.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Treatment
A hearing specialist can help you find the best hearing loss treatment options for your unique needs. Many patients with sensorineural hearing loss find success with hearing aids. Modern hearing aids deliver amplified sound directly to your ear, while also enhancing overall sound quality, and even suppressing distracting background noise. This can instantly improve daily communication by making it easier to understand speech and restore the level of independence and quality of life that you deserve.
Continued care through annual hearing exams and hearing aid adjustments is essential for maintaining your long-term hearing health. Working with a hearing specialist to monitor your hearing allows for appropriate treatment adjustments to be implemented as needed.
Schedule a Hearing Test at a Clinic Near You Today
Sensorineural hearing loss is a common condition that can severely impact your quality of life. Early diagnosis means earlier treatment and the skilled professionals at Audibel are here to give you the care you deserve. Find a hearing clinic near you to schedule a hearing test today.






Have a question or Comment?