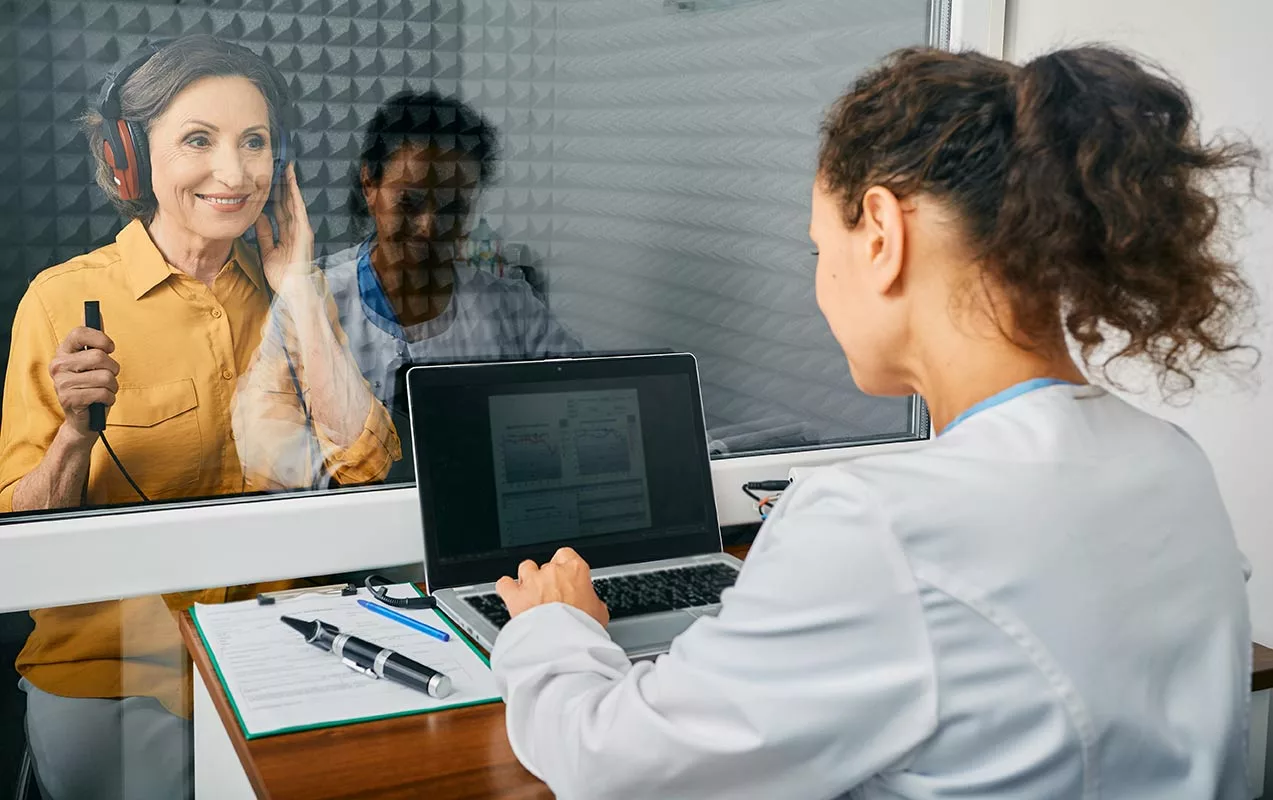

Hearing is an essential part of how we communicate and engage with the world around us. However, it’s natural for our hearing ability to change as we age, often due to environmental factors like noise exposure, or the aging process itself. So, what is a normal hearing range then?
Keep reading to learn what is considered a normal hearing range for adults, and how specialists evaluate your hearing health overall.
What’s Considered a Normal Hearing Range?
A normal hearing range or healthy hearing range is the absence of hearing loss. Hearing loss is diagnosed using two key measurements:
- Decibels (dB): the loudness of a sound
- Frequencies (Hz): the pitch of a sound
Together, these measurements help determine whether a person has normal hearing or if there is any degree of hearing loss present.
Decibels (dB): Measuring Loudness

Decibels (dB) measure the intensity or loudness of sound. The lower the decibel level, the softer the sound, while higher decibel levels indicate louder sounds.
A normal hearing range in adults typically falls between -10 dB to 20 dB.
A person with a healthy hearing range will be able to hear soft sounds like the sound of someone breathing or whispering. The table below outlines different decibel levels and common sound comparisons:
| Decibels (dB) | Sound Comparison |
|---|---|
| 10 dB | Someone breathing |
| 30 dB | Whispering speech |
| 60 dB | Typical conversations |
| 80 dB | Power tools, passing motorcycles |
| 100 dB | Live music concert, chainsaw |
| 120+ dB | Jack hammer, fireworks, jet engine |
Any sound over 70 dB has the potential to cause hearing loss over time. The louder the sound is, the less time it will take for permanent damage to occur. For instance, any sound 120+ dB can cause instant hearing loss.
Frequencies (Hz): Measuring Pitch
Sound frequencies are measured in Hertz (Hz) and are closely related to how we perceive the pitch of a sound. Lower frequencies produce deeper sounds (like a bass drum), while higher frequencies create higher-pitched sounds (like a bird chirping).
An adult with normal hearing can typically hear frequencies ranging from about 20 Hz up to 20,000 Hz.
The ability to hear higher frequencies often declines with age, greatly reducing speech clarity. The table below outlines different frequency ranges and common sound comparisons related to vocal ranges and speech:
| Frequency (Hz) | Sound Comparison |
|---|---|
| 250 Hz – 500 Hz | Low-pitched or deep voices, most vowels in speech |
| 1,000 Hz – 2,000 Hz | Mid-range frequencies essential for many speech sounds |
| 4,000 Hz – 8,000 Hz | Higher-pitched sounds or voices, many consonants in speech like “s,” “f,” and “th” |
For many people, one of the first noticeable signs of age-related hearing loss is difficulty distinguishing certain consonants (“s,” “f,” and “th”). It’s also incredibly common to struggle to hear higher-pitched voices like those of women and children.
How Your Hearing Range is Tested
To find out what your hearing range is, all you need is a comprehensive hearing evaluation. During a hearing test, you will undergo a series of simple assessments including:
- Pure Tone Test: measures how well you can hear sounds at different loudness levels (dB) and frequencies (Hz).
- Speech Threshold Test: determines the softest level at which you can understand spoken words.
- Speech Comprehension Test: measures how well you can recognize and process various syllables.
- Sound Filtering Test: gauges how well you can isolate speech amid noise.
- Bone Conduction Test: helps determine the type of hearing loss (conductive or sensorineural) by measuring how well sound travels to the inner ear.
These results are then plotted on a graph called an audiogram, which shows the softest sounds you can hear at each frequency. Your hearing healthcare specialists use this information to determine whether your hearing falls within the normal range or if hearing loss is present and to what degree.
The table below outlines common hearing level classifications and their corresponding decibel ranges:
| Hearing Level | Decibel (dB) range of the softest sounds a person can hear |
|---|---|
| Normal Hearing | -10 dB – 25 dB |
| Mild Hearing Loss | 26 dB – 40 dB |
| Moderate Hearing Loss | 41 dB – 55 dB |
| Moderately Severe Hearing Loss | 56 dB – 70 dB |
| Severe Hearing Loss | 71 dB – 90 dB |
| Profound Hearing Loss | 91+ dB |
The Importance of Routine Hearing Tests for Adults
Hearing loss often develops gradually, making it harder to notice symptoms until they become severe. Even if your hearing seems fine, regular hearing exams help detect early changes in your auditory health so you can get the timely care you deserve.
Baseline Hearing Tests
Having a hearing test done before hearing loss has occurred will provide you with a hearing baseline. This test will ensure even the smallest changes in your hearing are identified early, and treatment can be implemented as soon as possible.
Regular hearing tests also allow specialists to identify signs of hearing damage, typically caused by exposure to loud noise (noise-induced hearing loss), medications (ototoxicity), or other environmental causes. By identifying these potential risks, preventive measures can be implemented to safeguard your hearing and prevent further damage.
How Often to Get Your Hearing Tested
How often you should get your hearing checked can vary depending on various factors, including age, overall health, and risk factors:
- Ages 18-40: For adults under 40 years old and in overall good health, hearing tests are recommended every 3 – 5 years.
- Ages 40–60: After the age of 40, having a hearing test every 1–3 years is highly advisable.
- Ages 60+: Annual hearing exams are recommended for everyone over the age of 60.
- High-Risk Individuals: Annual hearing tests are highly recommended for people exposed to loud noise regularly, those who have a family history of hearing loss, or have an underlying health condition that can affect hearing.
- People with Hearing Loss: Annual hearing tests are essential for anyone already experiencing hearing loss.
Your Journey to Better Hearing Starts at Audibel
If you or a loved one have noticed recent changes in your hearing, scheduling a hearing exam is vital. Early detection of hearing loss plays a crucial role in reducing the impact of the condition on your daily communication and quality of life.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—find an Audibel hearing clinic near you today.






Have a question or Comment?